You are convinced of VR or have at least experienced the advantages of virtual reality in some form. Now do you want to know specifically what the practical application looks like? In the last article about VR, the application in factory planning was briefly discussed. This article will now go into the use of visTABLE®VR in more detail. You can find out in the article what you need and how VR supports you in layout planning with visTABLE®.
Why can a VR app add value to layout planning?
- Presence – The simple fact that you feel like you are standing in your factory in VR. You perceive the 3D model at the correct dimensions and distances. This is convincing and understandable.
- Acceptance – Employees can experience their workplace very realistically before construction and get a good feel for the planned environment
- Improved error analysis – the special features of virtual reality make it easier to check the installation plan
VR can provide a very clear and realistic image of the current or future state of your factory, thus expanding the 3D view. This improves communication for everyone involved.
Possible configurations for a VR app
The most attractive form of operating VR from a user perspective can be briefly described as follows:
- mobile – change of location possible at any time, easy setup and set-up
- wireless – can be operated via wireless LAN (WLAN) for the image and control data
even better or ideal:
- self-contained – standalone Head-Mounted Display (HMD) with integrated computer
The following illustration shows three possible configurations. From the left, often permanently installed, to the right, independent, mobile at any time. Everything can now be operated at a reasonable cost and has long since found its way into private entertainment.

The middle configuration in the picture represents a good compromise between mobility and computing power. With markerless inside-out tracking and a VR notebook, you can switch to another room within a few minutes to start the VR app. The studies by VDC Fellbach on tracking accuracy also show how well markerless inside-out tracking works. The technology has now established itself on the VR market and is used in numerous VR glasses.
Independent operation on the glasses alone is possible, for example, with the Prospect software from IrisVR. However, this requires prior 3D scene export and the use of a cloud resource and does not correspond to direct VR use. Small to medium-sized layouts with several million areas can currently be displayed on mobile devices. With optimized 3D data, this roughly corresponds to a medium-sized factory. However, with a powerful notebook with the latest CPU and GPU generation, 5 to 10 times the model size can be achieved. In addition, a direct connection to the planning software can be implemented using a PC, as is possible in visTABLE®VR.
Wireless use via Wi-Fi 6 (IEEE 802.11ax) is standard today. The local conditions for small latencies must be taken into account. In particular, distances between router-notebook-HMD are crucial and that all devices also have access to the common network. Ideally, a LAN cable is used between the router and the notebook in order to obtain a smooth VR image signal. The distance from the router to the VR glasses should not exceed 5m. In addition to these technical hurdles, the VR software must also support wireless use, as in the case of visTABLE®VR.
Graphics performance hardware
BThe hardware requirements depend on various factors:
- of the application – simple or complex 3D factory layout
- the VR glasses used – low or high resolution
- the accepted refresh rate – 45Hz with intermediate frame calculation or ideally 90Hz native and more
VR laptop
The website notebookcheck.com offers a good overview of laptop graphics cards from Nvidia and AMD, divided into performance classes:
Complex layout / high resolution and refresh rate: performance class 1. High-end graphics cards
Simple layout / low resolution and refresh rate: the top 30 GPUs in performance class 2. Midrange graphics cards
Processor: suitable for the graphics card, performance of the notebook
RAM: 16/32GB
The graphics card in particular is required for large 3D models from the factory and should be able to calculate high refresh rates in VR. On the one hand, this is important for user comfort to avoid so-called motion sickness, but also for the usability of software functions in VR. A computer can never be fast enough for VR applications, due to the necessary double image calculation for the left and right eyes and even if you are working with 3D CAD product data that is not fully optimized. So you at least still have a certain performance buffer to compensate for weaknesses in the 3D model. However, it is advisable to check the 3D data beforehand, especially for a VR app.
Uncompromised performance with a desktop system
If mobility is not an issue for you, a desktop system may be an option. This way you can achieve even more graphics performance for VR display. At Nvidia, this primarily affects the top model RTX 4090 (as of May 2024), which offers significantly more performance compared to the laptop GPU of the same name. In addition, native, wired PCVR glasses do without compression and decompression of the image signal, which leads to lower latencies and slightly higher image quality.
VR glasses
The Meta Quest 3 is currently a good choice if you want to operate VR wirelessly and are looking for very good image quality. It can be operated via a link cable as well as Air Link, Steam Link or Virtual Desktop in conjunction with a notebook or desktop PC. If you are a single user and always use the glasses wired in the same place, there are numerous alternative VR glasses. Mixed or VRcompare, for example, also provide a good overview.
If you already use other VR headsets in your company, simply check compatibility with visTABLE®VR and whether the device meets your needs. The Meta Quest 3, HP Reverb G2 or the HTC Vive Cosmos definitely work.
Basically, VR glasses on the PC differ as follows:
- Wired or can also be used wirelessly
- Marker-based or markerless inside-out tracking
- possible resolution and refresh rate
- Lens design and associated sweet spot
- Display type, LCD or OLED
- Easy or complicated to set up and operate
- Adjustability IPD, fixed, in steps or freely adjustable
Software for the VR app
visTABLE®VR
Enables seamless opening of visTABLE layouts (vtlx files) without third-party software.
Three steps to use visTABLE®VR
- Create a layout with visTABLE® and save it. If you already have a saved 3D layout, then you can skip this step. Otherwise, plan as usual with visTABLE® and save the layout as a vtlx file.
- Turn on your VR glasses. You should be sure that the VR glasses are ready for use. You can ensure this, for example, by successfully using another VR application on this PC.
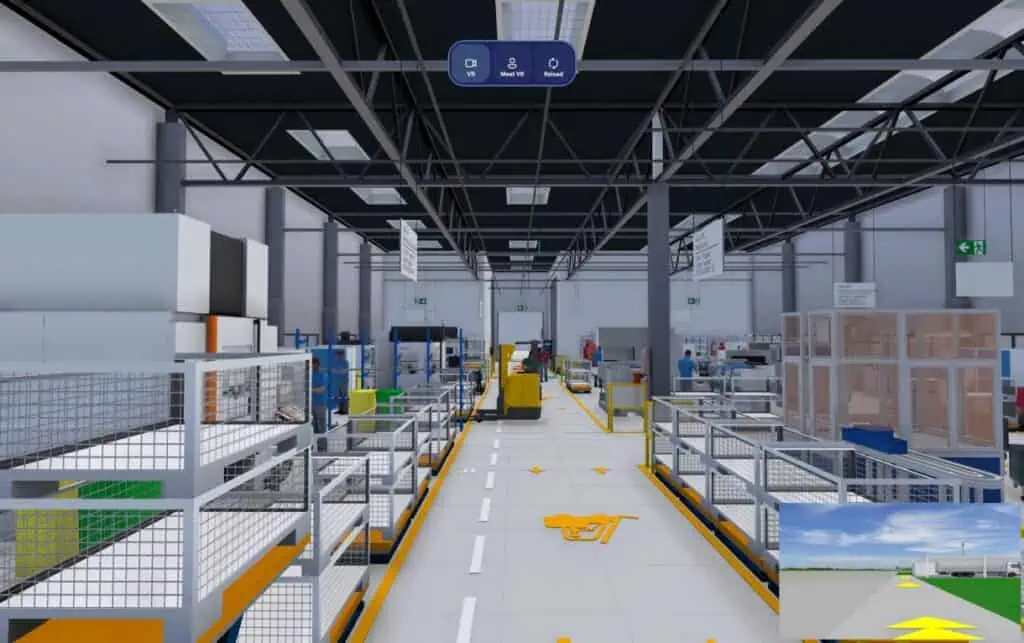
- Start visTABLE®VR and after a certain loading time you should be able to see your 3D layout in VR.
You can now navigate your layout using teleport or even fluid movement. It is also possible for a second user on the desktop to meet with you in VR. To do this, the “Desktop” function is activated. Navigation works with the WASD keys (move) + left mouse button (rotate), hold down and move. To meet in VR, call up the “Meet VR” function
No problem, simply subscribe to our Blog-News!