Cardboard Engineering is a lean management method for designing workplaces on a 1:1 scale using cardboard or wooden models. This is carried out as a workshop involving the people who (will) work at the workplaces. Therefore, the Cardboard Engineering solutions are well accepted. In addition, production and processes benefit from the ideas and experience of the employees.
The benefits of Cardboard Engineering
The method is of great importance in manual or partially automated assemblies that are developed in teams according to lean principles. This is because lean production requires very flexible work systems. The aim is to provide materials and resources at the best point. Round tube constructions or industrial profiles are used for this purpose. This is because best-point provision throughout the entire process often requires unconventional solutions. These are easy to implement with modular systems. They are also used in a variety of ways in lean production, e.g. for flow racks or setup trolleys.
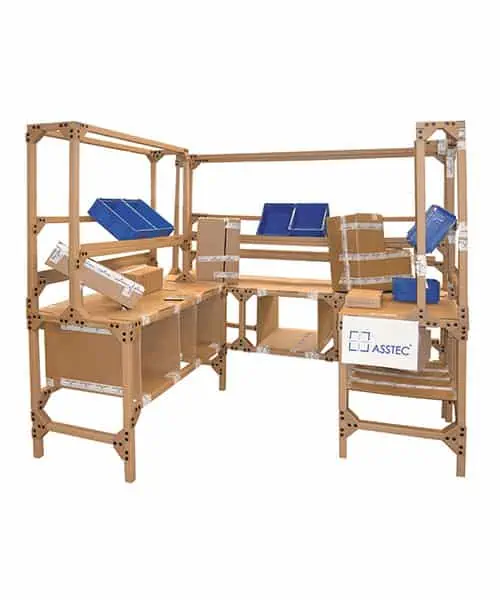

Cardboard models are also used for the continuous improvement of various work systems in manufacturing companies. Because before expensive prototypes are created, cardboard workshops strengthen the understanding of those involved. Even under the influence of the Digitalization of production, the focus is still on trying out new work systems with real operating equipment, or perhaps precisely because of this.
Limitations of Cardboard Engineering
Major drawbacks of Cardboard Engineering workshops are their space, time, and staffing requirements. However, as with many lean tools, time and personnel costs can be offset by saving on specialist engineers and leveraging employee expertise. In addition, numerous consulting formats are available to assist companies in implementing this and other lean tools.
What cannot be compensated, however, is the space required. After all, cardboard models can only be used effectively on a 1:1 scale. After all, real work situations are to be simulated with them. It is not uncommon for many square meters of production area to be simulated. For iterative optimization of processes or ergonomics, the set-up must sometimes be kept for several days. All this limits the field of application to the design of individual workstations or smaller lines without automation.
As soon as more extensive processes have to be planned in the factory layout, the digital world has a clear advantage. Today, digital systems also enable participative developments in workshop formats. This means that the acceptance and teamwork effects of Cardboard Engineering can also be used in applications for factory layouts.
Conclusion
Cardboard Engineering is among the first choices for the collaborative development of manual work systems. Even though established engineering methods using digital models can lead to comparably good solutions more quickly, they have two decisive disadvantages:
- They are reserved for experts (e.g., MTM users, CAD designers, simulation users) or require their tools.
- They do not involve stakeholders in the development and optimization of production to the extent that a lean workshop with cardboard engineering does.
Due to the high space requirements and the lightweight materials used, the efficient application of cardboard engineering in the company is limited to smaller work systems with low handling masses. Manual assembly is a good example of this.
Related topics:
- Teamwork in shopfloor layout planning
- Planning an assembly line – 5 key aspects
- The importance of space utilisation and design in your factory
- Assembly planning
No problem, simply subscribe to our Blog-News!